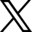You
Arcadian IoT
Sector
Other
Artificial intelligence
Internet of things
Mobile apps
Web apps
Challenge
ARCADIAN – IoT aimed to drive the evolution of IoT systems towards decentralized, transparent, and user-controllable privacy. Three practical use cases will be done to demonstrate its applicability to real world solutions. One of these use cases focuses on the use of drones and IoT technology for emergency response and surveillance. The goal is to demonstrate how the Arcadian IoT platform can help improve emergency response and surveillance scenarios.
Our approach
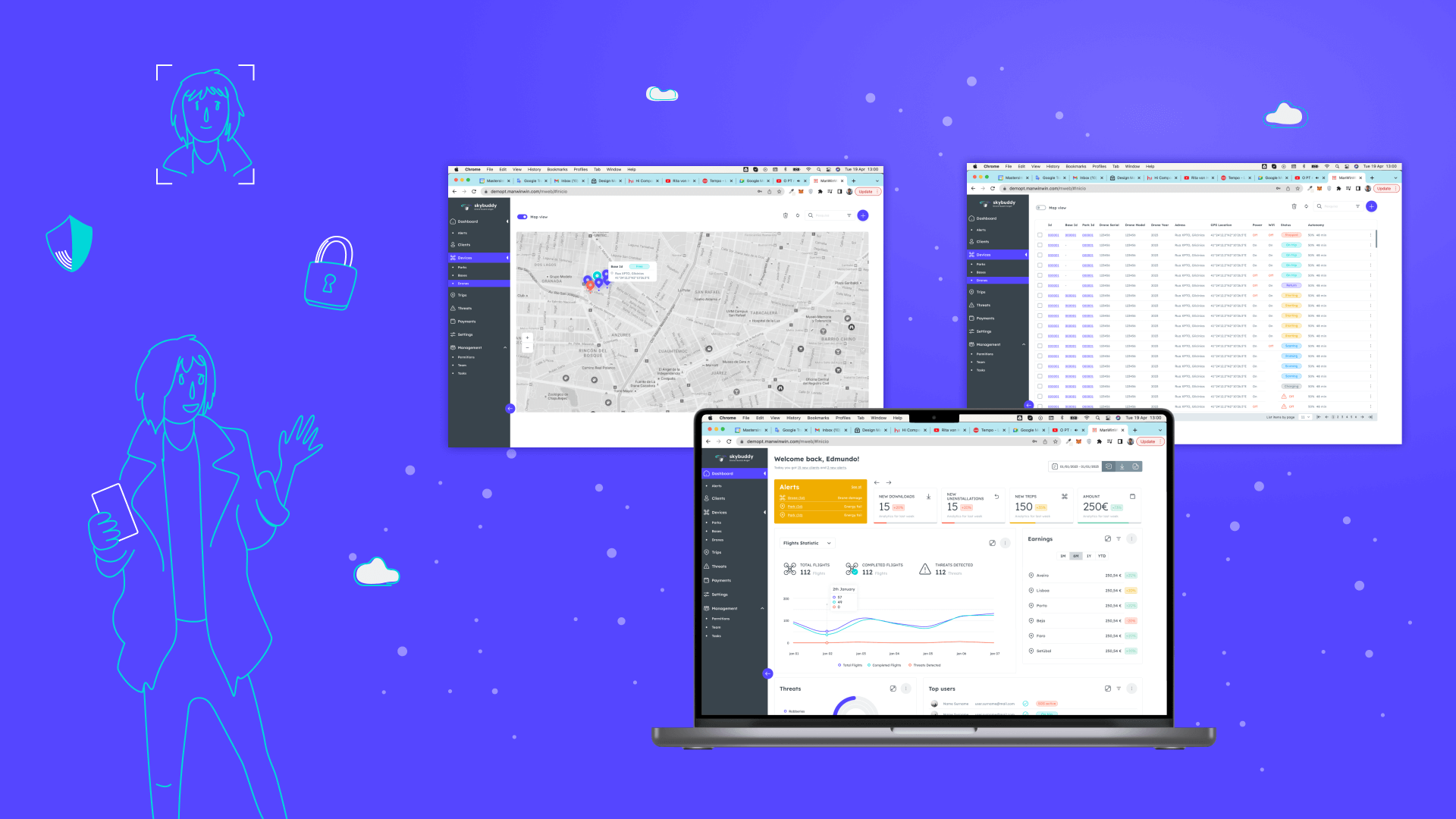
Introducing Drone Guard Angel (DGA), a service that enables drones to track and monitor people during their daily activities in urban areas. Let us imagine a scenario in which a young woman, after having dinner with friends, requests the assistance of a Drone Guard through the corresponding app on her smartphone. Once she authenticates, a drone stationed nearby verifies her identity and escorts her home. Throughout the journey, the Drone Guard Angel (DGA) diligently surveils and detects potential threats such as rapid movement or suspicious objects. AI models process image recognition to detect anomalies. In case of anomalies, the drone initiates deterrence maneuvers, alerts authorities, and summons a rescue team in case of injuries. Meanwhile, the drone collects important data, including location details and images, to aid in later investigations.
This domain of implementation covers trust, security, and privacy challenges, meeting the Arcadian-IoT objectives, such as:
- The protection of individuals’ and objects’ identities is ensured by several measures, such as the explicit consent of individuals, to ensure that their privacy rights are respected, including the collection of images, which strictly adheres to privacy and drone regulations. In addition, multi-level authentication is required for all devices involved in the process. These devices must be registered on the platform, which further increases security and control. Additionally, encryption mechanisms are implemented to protect information during communication, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure data confidentiality.
- Secure authorization is established both between drones and objects and between drones and individuals, through a robust authentication process. To achieve this, a comprehensive system with multiple levels of authentication is implemented. Similarly, individuals interacting with the drones are subjected to the necessary authentication measures to establish their identity and authorization. By requiring secure authentication and authorization, the system ensures that only authorized drones can access and interact with specific objects or people.
- Local intelligence is used in the application to protect the privacy of individuals and prevent the disclosure of private information. This is possible thanks to the use of AI models that work within the app and/or the drone itself. These models are responsible for detecting potential threats in privacy-sensitive situations.
Additionally, self-encryption mechanisms are implemented to protect data stored locally in drones. In cases where drones are storing images or video for potential use by the justice system, the self-encryption mechanisms provide an additional layer of protection for sensitive information. - Autonomous security mechanisms, including intrusion detection and prevention systems, are critical to ensuring the cybersecurity of IoT devices. They actively detect and mitigate potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. Recovery solutions address physical threats and improve protection against risks such as drone theft.
- Denial of Service (DoS) from servers that provide support for drones. It is critical to protect and strengthen cloud-hosted or edge services by implementing robust protections and building in self-healing mechanisms. These defenses are especially important to withstand high-impact attacks and ensure uninterrupted functionality.
Scroll to the end of the gallery to see a video about this case study.
Solution
The Drone Guard Angel (DGA) solution uses an IoT device to deliver its services to individuals, who are required to have a personal device such as a smartphone in order to access the service. Additionally, the solution relies on the use of sensitive personal data, including location, address, and photos, for facial recognition purposes. As a result, challenges pertaining to trust, security, and privacy management arise. Some of these challenges include:
- Ensure security and trust in the management of drones’ and users’ identification, safeguarding against impersonation attacks that pose risks to both personal safety and data security.
- Define trust evaluation models for DGA devices, services, and applications, providing end-users with awareness of the reliability and trustworthiness of system components.
- Safeguard users’ and devices’ sensitive data (such as authentication credentials, location, course/path, and photos) through robust encryption mechanisms that offer recovery capabilities.
- Evaluate the integrity and identify anomalous behavior in IoT devices (drones) and associated services, enabling the detection of known or zero-day vulnerabilities and threats.
- Implement autonomous self-recovery mechanisms within the DGA ecosystem (including app services and related data) to restore functionalities and data to predefined trust levels in the event of incidents with drones or personal devices, reducing the need for extensive human intervention.
- Enable an automated and privacy-preserving approach to cyber threat intelligence (CTI) for the generation, sharing, analysis, storage, and consumption of IoT threat information.
Skills &
Technologies
Results
This is an ongoing project in development aimed at demonstrating the feasibility of its technology and its potential application in civil society. The goal is to reach Technology Readiness Level (TRL) 6, which entails creating a prototype/demonstrator that serves as the basis for designing a business model and formulating a production plan to adapt it to the market. There are additional challenges to address, including drone legislation, which will be analyzed in a subsequent phase and scope of the project.